
AP U.S. Government & Politics
Assignments
AP U.S. Government & Politics
Assignments
AP U.S. Government & Politics

AP U.S. Government & Politics
Practice materials
AP U.S. Government & Politics
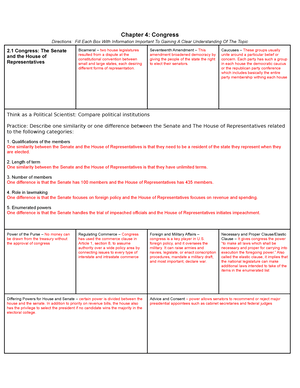
AssignmentsArticle II – The president can recommend legislative measures to congress, veto or approve proposed bills from article 1, and convene or adjourn the houses of congress. The framers also created a system by which the Electoral College chooses the president every four years.
Formal Powers – the president exercises the formal powers of the office those defined in article II .
Informal Powers – As well as the informal powers those political powers interpreted to be inherent in the office to achieve policy goals.
Chief Legislator – term for the president as architect of public policy and the one who sets the agenda for congress
Powers of Persuasion – the president uses a number of skills to win support for a policy agenda. The president will use bargaining and persuasion to get congress to agree with and pass the legislative agenda
Veto – To reject or prohibit action and laws of other government officials checks and balances a system that balances the distribution of power in a government
Pocket Veto – A veto taking place when congress adjourns within 10 days of having submitted to a bill to the president who simply lets it die by neither signing nor vetoing it
Line-Item Veto – This measure would empower an executive to eliminate a line of spending from an appropriations bill or a budgeting measure, allowing the president to veto part, but not all, of the bill.
Commander in Chief -The role of the president as supreme commander of the military forces of the United States and of the state National Guard units when they are called into federal service
Executive Agreement – It is a simple contract between two heads of state: the president and a prime minister, king, or president of another nation.
Executive Powers and Policy -- The Panama Canal - The policies of two presidents regarding the Panama Canal show two very different ways of using the powers of the executive branch to advance a policy agenda and interact with Congress
Executive Orders – empowers the president to carry out the law or to administer the government. Unlike a criminal law or monetary appropriation, which require congress to act, a presidential directive falls within executive authority.
Signing Statements - These statements explain their interpretation of a bill, their understanding of what is expected of them to carry it out, or just a commentary on the law.
Executive Privilege - the right to withhold information or their decision-making process from another branch, especially Congress.
President can exercise formal powers of the office those in article II as will informal powers to achieve policy’s agenda.
The President’s Term - Constitution gives the president the power to assemble that group and “. appoint ambassadors, other public ministers and consuls and all other officers of the United States whose appointments are not herein otherwise provided for and which shall be established by law.”
The Vice President - Declares that in care of presidential removal, death, resignation, or inability, the presidents duties and powers “shall devolve on the vice president
Cabinet - a formal body of leaders or department heads who act as government advisors
Secretaries - modern presidents create some balance based on geography , gender, ethnicity, and even partisan ideology.
Ambassador - an official representative of a country's government
Chiefs of Staff - a council of the top informed officials from each division advises the president on military strategy.
Federal Agencies - are subcabinet entities that carry out specific government function -executive agency, military department, a court of the united states
White House Staff - the presidents immediate staff of specialists makeup the white office. These require no senate approval and tend to come from the presidents inner circle or campaign
Chief of Staff - tend be tough, punctual, detail-oriented managers, and these qualities allow the president to concentrate on big picture decisions.
Inherent Powers - powers that a sovereign entity can assume to have as a necessary to the work ability of the government or office
The Senate and Presidential Appointees - occasionally high- level appointees are subjected to senate investigation and public hearing. Most are still approved while a few will receive intense scrutiny and media attention and some appointment with fail
Senate Standoff - senate disagrees with presidents staff
Ambassador Appointments - the senate is also likely to confirm ambassador appointments although those positions are often awarded to people who helped fund the president's campaign rather than people well qualified for the job
Stewardship Theory Approach to governing presumed the president had a duty to act.
Franklin Delano Roosevelt President during great depression and new deal
War Powers Act Maintains the presidents needs for urgent action and defense at the US while preventing war authority.
Bully Pulpit A prominent stage from where ideas can be pitched to the American people
State of the Union Address
Spin and Manipulation
Obama Embraces New Media Hired a 30-year-old new media director
Image Control Congress basically hires photographers to make the president look good